High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are both types of polyethylene plastic but have different properties and applications.
- Density and flexibility
HDPE- it has a higher density (0.941-0.965 g/cm3) and is more rigid. It feels stiffer and more robust.
LDPE– it has a lower density (0.910-0.940 g/cm3) and is more flexible. It feeds softer and more pliable.
- Transparency
HDPE- it is typically more opaque. It has a matte finish and is less transparent.
LDPE– usually more translucent or even transparent, with a shiner surface
- Surface feel.
HDPE– feels smoother and less stretchy
LDPE– feels waxy and can stretched easily without tearing
- Application
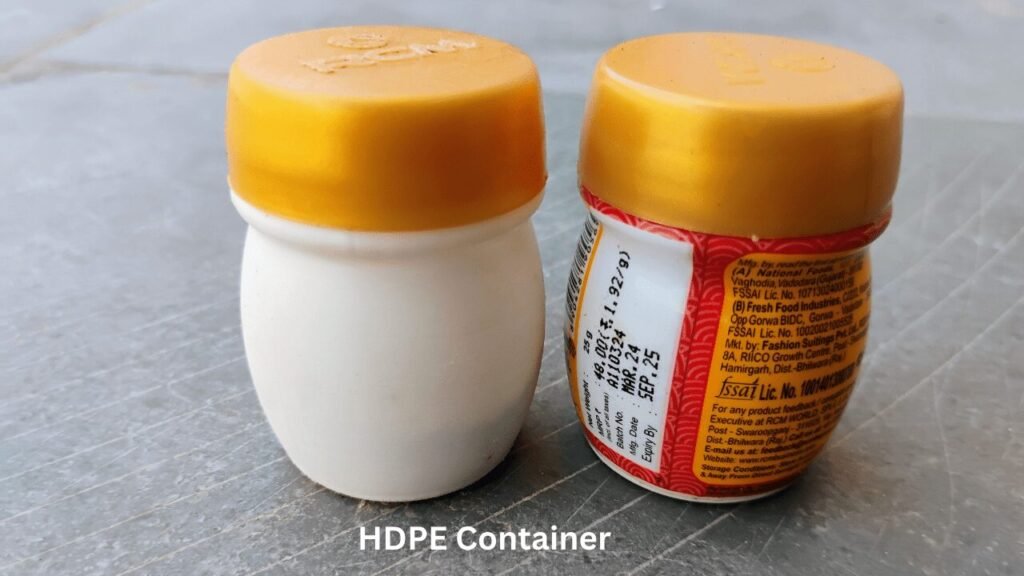
HDPE– it is commonly used in items like plastic bottles, milk jugs, detergent bottles, and piping, HDPE Containers.
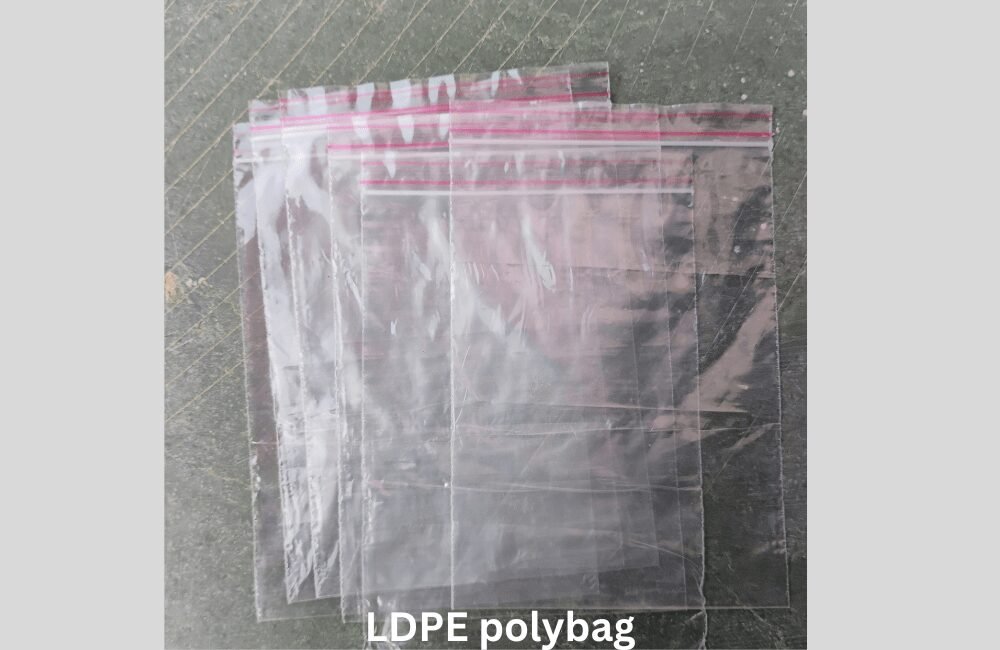
LDPE– it is often used in plastic bags, shrink wrap, and squeezable bottles
- Melting Point
HDPE– it melts at higher temperatures around 130-1370c
LDPE– it melts at a lower temperature around 105-1150c
- Sound
HDPE– when crumped, it produced a “sharper” sound due to its rigidity.
LDPE- when crumpled, it produces a “softer” sound due to its flexibility
- Burn test
HDPE– burn with a blue flame with a yellow tip, producing a waxy smell. It drips when burning and continues to burn after removing the flame.
LDPE– burn with a similar flame to HDPE but is more prone to dripping. The smell is also waxy and it burns more quickly
- Identification code
HDPE– typically marked with a recycling code of #2
LDPE– typically marked with a recycling code of #4
9. Identification by FTIR
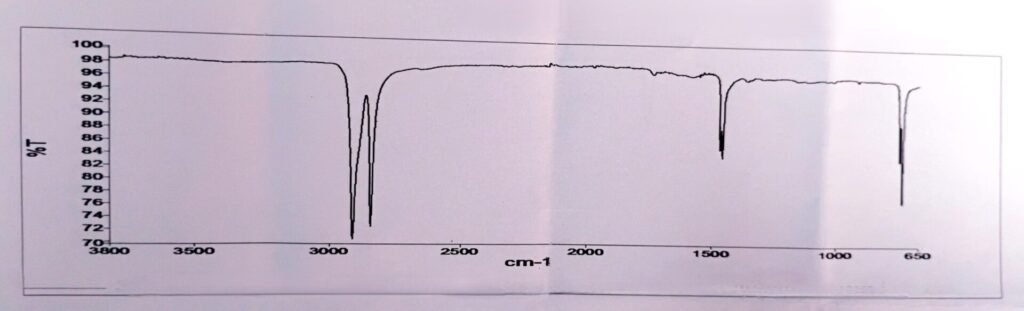
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) FTIR Graph
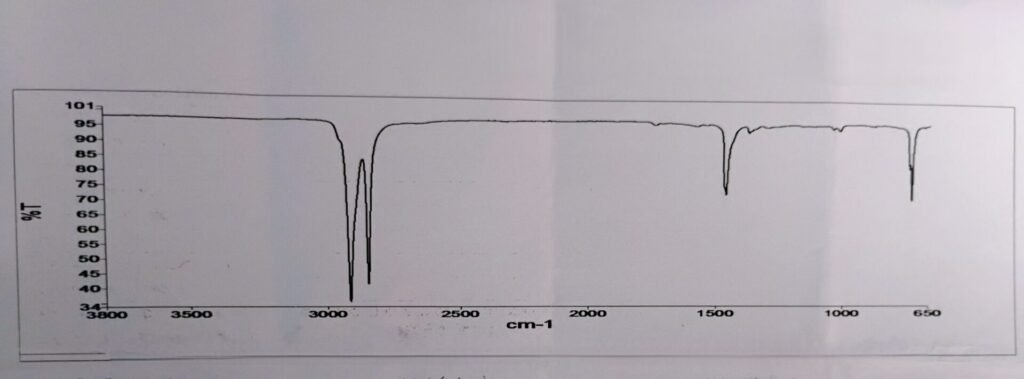
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) FTIR Graph
Why HDPE is more rigid than LDPE
HDPE is stronger than LDPE due to differences in their molecular structure, crystallinity, and intermolecular forces. The combination of a more linear molecular structure and higher crystallinity in HDPE results in a material that is generally strong, stiffer, and more resistant to compare to the more branched and less crystalline LDPE.


- Molecular structure
HDPE– It has a more molecular structure with very little branching. The polymer chain is packed closely, allowing strong intermolecular forces (van der Walls forces) to act between the chains. This close packaging leads to a higher density and greater rigidity.
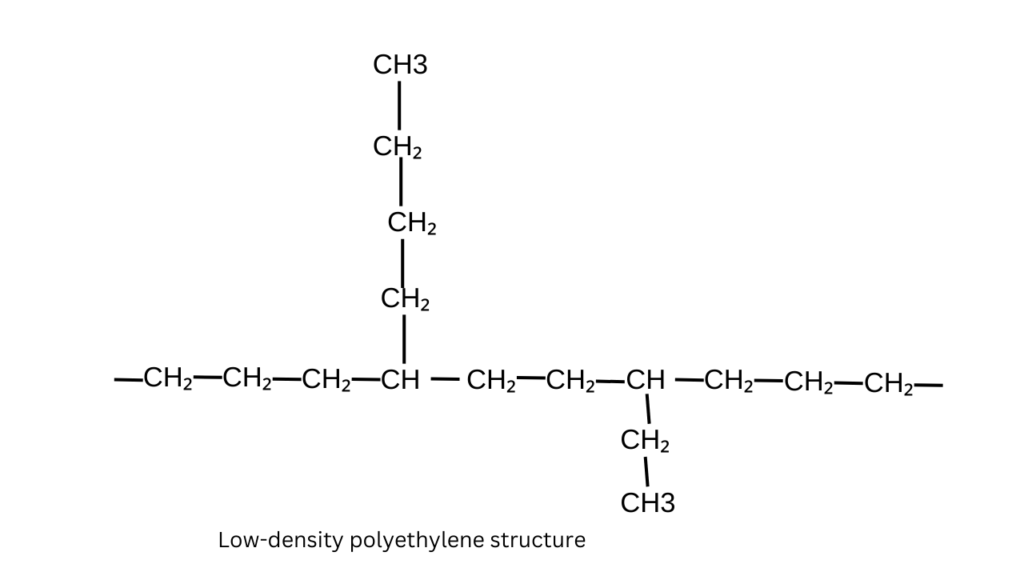
LDPE– it has a highly branched molecular structure, the branches prevent the polymer chains from packaging closely together, leading to a weaker intermolecular. This looser packaging results from a lower density and more flexible material.

2. Crystallinity
HDPE– the linear structure allows HDPE to form a higher degree of crystallinity, where the polymer chains or organized in a regular, repeating pattern. This crystalline structure contributes to the material’s rigidity and strength.
LDPE– the branched structure leads to lower crystallinity, with a more amorphous arrangement of polymer chains. This amorphous structure makes LDPE softer and more flexible.
3. Intermolecular forces
HDPE- the strong intermolecular forces between the closely packed polymer chains make HDPE tougher and more resistant to deformation.
LDPE– the weaker intermolecular forces due to the branched stricter make LDPE more and less rigid
I am Maneesh Maurya a professional pharmaceutical blogger from India having rich experience in the pharmaceutical Quality control field.




[…] plastic packaging options are available and can be produced using high-density polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), polyethylene (PP), Polyethylene terephthalate […]
[…] (high-density polyethylene) is directly in contact with drugs it is a primary packaging material. HDPE is a thermoplastic polymer made from petroleum. Its outstanding tensile strength and large […]
[…] are different types of materials in use. The composition of the material is 50% to 60% (w/w) of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), 30 % to 40% (w/w) of ethylene alcohol (EVOH), and 10 to 20% (w/w) of at least one compatibilizer, […]
[…] packaging material. Ldpe for short is a type of thermoplastic made from the monomer ethylene. LDPE bags are more flexible than other bags because they have excessive branching with very low density, […]