HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is directly in contact with drugs it is a primary packaging material. HDPE is a thermoplastic polymer made from petroleum. Its outstanding tensile strength and large strength-to-density ratio. HDPE container has a heavy impact resistance and melting point.

HDPE containers are mainly two types either cloudy white or solid colored. Its container is one of the most widely used packaging materials and is used for everything from rigid containers. It is popular for its versatility and its protection against contamination. HDPE closures are also connected with containers in pharmaceutical finish products like, tablets, capsules, ointments, creams, etc.
Its HDPE container quality is better so we are following some testing parameter
Table of Contents
1. Description
Take the sample visually and check the color, design, and threaded neck.
2. Dimension:
- Total height: Take 5 selected samples and measure the Total height with a calibrated Vernier caliper. Take reading and Note down reading.
- Outer diameter: Take 5 selected samples and measure the outer diameter with a calibrated Vernier caliper. Take reading and Note down reading.
- Inner diameter: Take 5 selected samples and measure the Inner diameter with a calibrated Vernier caliper. Take reading and Note down reading.
- Midpoint thickness: Take 5 selected samples and cut by cutter, measure the midpoint thickness with a calibrated Vernier caliper. Take reading and Note down reading.
- Neck height: Take 5 selected samples and measure the neck height with a calibrated Vernier caliper. Take reading and Note down reading.
3. Total weight:
Take 5 selected samples weigh them one by one put them on the calibrated analytical balance. Take a printout of the weight.
4. Multiple Internal Reflectance:
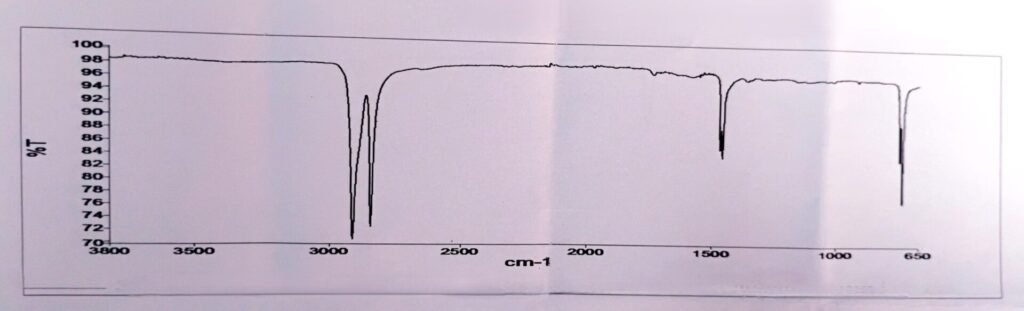
HDPE containers are made from polymer their polymer is made single polymer or mixed polymer they are identified by the multiple internal reflectance. Its test is performed by the FTIR instrument. This container is made from HDPE. The standard is the HDPE Reference standard. The standard is a graph plotted between the wavelength 3800-650 cm-1. The sample is also plotted 3800-650 cm-1.
The corrected spectrum of the specimen exhibits major absorption bands only at the same wavelength as the spectrum of the high-density polyethylene reference standard.
5. Light transmission:
the light transmission test is perform, Take the HDPE container cut by the cutter of a suitable size. Wash and dry taking care to avoid leaving fingerprints or other marks on the surface area of the sample through which light must pass.
In the UV instrument set spectrophotometer mode wavelength 290 to 450 nm in transmittance mode. First blank scan at wavelength 290 to 450 nm the reading 100% light pass. Then the sample is placed in the sample cabinet scan the sample is capable of measuring and recording light transmitted diffused as well as parallel rays.
The results in percentage. Not more than 10% in the wavelength 290 to 450 nm
6. Extraction Test
these are performed in 3 parts within different mediums. Another test performed for the non-volatile residue test, buffering capacity, and heavy metal.
these are performed in 3 parts within different mediums. For use as a sample for its extraction, the test is the non-volatile residue test, buffering capacity, and heavy metal. For use as a sample for it use
A. Extraction in water medium
B. Extraction in alcohol medium
C. Extraction in Hexane medium
take a glass stoppered 250 graduated cylinders type. Clean glass if necessary with hot nitric acid, followed by prolonged rinsing with water and clean cutting by the appropriate method (eg-successive cleaning with acetone and methylene chloride ) before use in subdividing a specimen clear all equipment by scrubbing with suitability detergent and rinsing with water. Its procedure is used in all extraction medium
A. Extraction in water medium: Take a sample and cut the equivalent of 120cm2 total surface area (both sides combined) it is subdivided into strips 5 x 0.3 cm. Take in a glass stopper add 70 ml water rinse the sample and drain off the water. Take in place a properly prepared sample to be listed in an extraction container and add 150 ml water. Extract container heating at 700c water bath at 24 hours.
Cool to about room temp. But not below 200 C.
B. Extraction in alcohol medium: Take a sample and cut the equivalent of 120cm2 total surface area (both sides combined) it is subdivided into strips 5 x 0.3 cm. Take in a glass stopper add 70 ml alcohol rinse the sample and drain off the alcohol. Take in place a properly prepared sample to be listed in an extraction container and add 150 ml alcohol. Extract container heating at 700c water bath at 24 hours.
Cool to about room temp. But not below 200 C.
C. Extraction in Hexane medium: Take a sample and cut the equivalent of 120cm2 total surface area (both sides combined) it is subdivided into strips 5 x 0.3 cm. Take in a glass stopper add 70 ml Hexane rinse the sample and drain off the Hexane. Take in place a properly prepared sample to be listed in an extraction container and add 150 ml Hexane. Extract container heating at 500c water bath at 24 hours.
Cool to about room temp. But not below 200 C.
7. NON-Volatile residue
this test is performed with the extraction test in the given medium.
- Non-Volatile in water medium: Taken tare Weight of the empty crucible (W1). Place 50 ml of the extracting medium in a water sample in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 700c until the water is dry. Some samples remain but the water is dry. Taken weight of the crucibles with sample (W2),
Wt. of sample = W2-W1= Ws
Taken another tare Weight of the empty crucible (W3). Place 50 ml of water in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 700c at till the dry water is in the crucible. Taken weight of crucibles with sample (W4),
Wt. of Blank sample = W4-W3= WB
Non-volatile in water medium = Ws- WB
The difference between the amount obtained from the sample preparation and the blank does not exceed 12.0 mg.
2. Non-volatile in Alcohol medium: Taken tare Weight of the empty crucible (W1). Place 50 ml of the extracting medium alcohol sample in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 700 c until the ethanol sample is dry. Some samples remain but the ethanol is dry. Taken weight of the crucibles with sample (W2),
Wt. of sample = W2-W1= Ws
Taken another tare Weight of the empty crucible (W3). Place 50 ml of ethanol in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 700 C until the dry ethanol is in the crucible. Taken weight of crucibles with sample (W4),
Wt. of Blank sample = W4-W3= WB
Non-volatile of water medium = Ws- WB
The difference between the amount obtained from the sample preparation and the blank does not exceed 75.0 mg.
3. Non-Volatile in Hexane medium: Taken tare Weight of the empty crucible (W1). Place 50 ml of the extracting medium in hexane sample in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 500 c until the hexane is dry. Some samples remain but the hexane is dry. Taken weight of the crucibles with sample (W2),
Wt. of sample = W2-W1= Ws
Taken another tare Weight of the empty crucible (W3). Place 50 ml of hexane in the crucible. Heating the crucible in a water bath at 500 C until the dry hexane is in the crucible. Taken weight of crucibles with sample (W4),
Wt. of Blank sample = W4-W3= WB
Non-volatile of water medium = Ws- WB
The difference between the amount obtained from the sample preparation and the blank does not exceed 100.0 mg.
8. Heavy metal:
the testing of heavy metal,Take two comparison test tubes of 50 ml. One sample is another for standard. Take a 20 ml extracting sample in water medium in one test tube. 20 ml water in the second test tube. Set the pH 3-4 with 1N acetic acid or 6N ammonium hydroxide, sample/Standard. Dilute with water up to 35 ml. 2 ml standard LED solution (containing 10ppm) and mix. Added 1.2ml thioacetamide glycerine base TS and mixed. After added with the solution Add 2 ml of acetate buffer of pH 3.5 and mix. Dilute up to 50 ml mix/ each cylinder Allow to stand for two minutes
View downwards over a white surface and compare the intensity of color in both. The color produced in the sample solution should not be greater than the standard solution. If the color produced in the sample solution is less than the standard solution, the sample will pass the limit test of heavy metals. The result is not more than 1 ppm.
9. Buffering capacity:
in this testing of buffering capacity, we determine the volume in ml. How many ml consumed in the sample reaches the 7 pH level of the sample. This test is performed with the help of an ATR instrument. When the water /extraction in water medium sample pH is less than 7 then use the 0.01N NaOH, or pH greater than 7 then use 0.01N HCL. The first test was in 20 ml blank (as a Water) solution titration with 0.01N NaoH/0.01N HCL. Then after titrating the sample with 0.01N NaoH/0.01N HCL.
Then the difference between the amounts obtained from the sample and the blank is not more than 10 ml.
10. DSC (differential scanning calorimetry) testing
cut the sample weighing about 12 mg and place it in the test specimen pan. When increasing the heating flow rate 20 C and 100 C per minute, it indicated an exothermic event. Then the sample absorbs the temperature more heat than the sample melts. When temp decreases in heat flow rate this is called endothermic. The temperature sensor measures a lower temperature for the sample compared to the reference.
DSC (differential scanning calorimetry) plot for the HDPE sample had been cooled to melt. The plot occurred during a temperature scan from 400 C and 2000 C.
Observation: the thermal analysis of the specimen is similar to the thermal analysis of HDPE RS. The melting temperature obtained from the thermal analysis of the sample specimen does not differ from the reference standard by more the 60 C
11. Environment stress crack resistance:
The environment stress crack resistance testing is first Taken 10% solution of containing teepol in SS tray in 6 HDPE Containers fill 3rd part teepol. In a hot air oven for 48 hours at 600c temperature.
The observation is the container does not have any crack/deformation of container on completion of 48 hours at 600c.
12. Overflow capacity
Take 5 samples of HDPE container. Fill with the water in an HDPE container overfill then measure the water in a measuring cylinder. Take reading and note down reading.
13.Resin:
there are defined HDPE containers in which the type of resin is used in manufacturing. It is easy to post-consumer recycled material. Mainly HDPE for use resin is PCR
14. Colorant:
there are mainly colors of the shade found in the container. There is which type of color formulation used in made containers example pigment, dye, and special effects color. There are sub-color variants: dry color, liquid color, paste dispersion, master batch, and compound color.
There are manufacturers defined in a certificate which colorants use.
15. Check for contamination:
the samples are visually checked the free them from dirt, foreign matter, or any other contamination both inside and outside. No scratch and colorant different from the container.
I am Maneesh Maurya a professional pharmaceutical blogger from India having rich experience in the pharmaceutical Quality control field.




[…] if more information about HDPE container testing procedure […]
[…] HDPE containers or plastic packaging materials are an integral part of pharmaceutical finish products to ensure their integral and self-life. Packaging material should not interact physically or chemically with the content in a way that identity, purity, stability efficiency, or safety is affected. Many packaging materials made from plastic polyethylene, polyolefin, and polyvinyl chloride are the most used pol […]
[…] HDPE containers are used in pharmaceutical and other industries. It is an important role given by HDPE containers. In its production, the manufacturer also ensures heavy metals like lead, cadmium, mercury, and chromium are as per given regulations. They are very toxic and can cause severe health problems, including neurological damage, kidney disease, and cancer. Ensuring that HDPE containers are free of these contaminants helps protect consumers from potential health risks. […]
[…] a sample of an HDPE Container portion of 120 cm2 total surface area (both sides combined). It is subdivided into 3mm in width and […]
[…] a sample of an HDPE Container portion of 120 cm2 total surface area (both sides combined). It is subdivided into 3mm in width and […]
[…] internal reflectance testing of HDPE containers performed with the help of an FTIR […]
[…] coils are used as fillers in bottles and containers to prevent damage to the shape of capsules and tablets, especially soft-gel […]